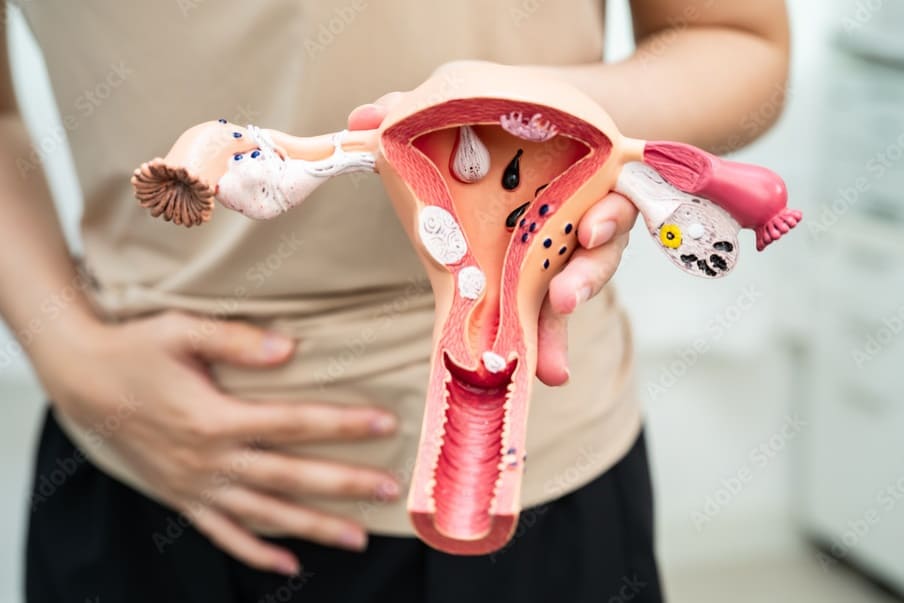
When it comes to women’s health, the uterus plays a crucial role in overall well-being. However, there are certain diseases linked to the uterus that, if ignored, can lead to severe complications—even life-threatening conditions. One such disease is uterine cancer, often overlooked in its early stages due to subtle symptoms. But it’s not just cancer; conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, adenomyosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can also have serious consequences if left untreated.
Why You Should Take Uterine Health Seriously
The uterus is central to reproductive health, but issues affecting it can impact much more than fertility. Ignoring symptoms can lead to chronic pain, excessive bleeding, complications in pregnancy, and, in severe cases, the spread of cancerous cells. Early detection is key, and a proactive approach to health can save lives.
Uterine Diseases That Must Not Be Ignored
1. Uterine Cancer
- This includes endometrial cancer, which starts in the lining of the uterus, and uterine sarcoma, a rarer type affecting the muscle and supporting tissues.
- Symptoms: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, unexplained weight loss, pain during urination or intercourse.
- Risk Factors: Obesity, hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, prolonged use of estrogen without progesterone.
- Why It’s Dangerous: If undiagnosed, cancer can spread to other organs, making treatment difficult and reducing survival rates.
- Prevention: Regular screenings, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing diabetes and blood pressure can lower risks.
2. Endometriosis
- A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic lining.
- Symptoms: Severe menstrual cramps, chronic pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, heavy bleeding, infertility, fatigue, bloating, nausea.
- Why It’s Dangerous: Delayed treatment can lead to infertility, ovarian cysts, and adhesions, which may cause organs to stick together.
- Prevention & Management: Hormonal therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in severe cases, surgery to remove excess tissue.
3. Uterine Fibroids
- Non-cancerous growths in the uterus, varying in size, often developing during childbearing years.
- Symptoms: Heavy or prolonged bleeding, frequent urination, pelvic pressure, constipation, back pain, painful periods.
- Why It’s Dangerous: Large fibroids can cause severe anemia due to excessive bleeding, complications during pregnancy, and may require surgical removal.
- Prevention & Treatment: Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing alcohol consumption, and treating with medications or surgery if necessary.
4. Adenomyosis
- A condition where the inner lining of the uterus grows into the muscular wall, causing painful and heavy periods.
- Symptoms: Severe menstrual cramps, prolonged periods, bloating, pain during intercourse, infertility.
- Why It’s Dangerous: Can lead to severe anemia, chronic pain, and increased risk of hysterectomy if untreated.
- Prevention & Management: Anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal therapy, or, in severe cases, hysterectomy.
5. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- An infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Symptoms: Pelvic pain, unusual vaginal discharge with a bad odor, fever, painful urination, irregular periods.
- Why It’s Dangerous: If left untreated, PID can cause permanent damage to the reproductive system, leading to infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
- Prevention & Treatment: Safe sex practices, regular STI testing, and prompt antibiotic treatment.
Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical advice immediately:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding (especially post-menopause)
- Severe pelvic pain that disrupts daily life
- Painful intercourse
- Unexplained weight loss or fatigue
- Frequent urination or constipation without any clear cause
- Persistent bloating or feeling of fullness
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Irregular menstrual cycles
Prevention & Early Detection: What You Can Do
- Regular Check-Ups – Get routine gynecological exams, including Pap smears, pelvic ultrasounds, and cancer screenings.
- Healthy Lifestyle – Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and engage in regular physical activity.
- Hormonal Balance – If you experience irregular periods, consult a doctor to rule out hormonal disorders and imbalances.
- Know Your Family History – Genetic factors play a role in uterine diseases, so share family medical history with your doctor.
- Listen to Your Body – Don’t ignore persistent symptoms. Early intervention is key to preventing complications.
- Safe Sexual Practices – Use protection and get regular STI screenings to reduce the risk of infections leading to PID.
Final Thoughts
Women’s health is often overlooked due to busy lifestyles or societal taboos. However, taking uterine health seriously can prevent major complications. If you notice any abnormal symptoms, don’t wait—consult a healthcare professional. Ignoring these warning signs could cost you dearly, and timely action can be lifesaving.
Also Read: