Dopamine has been called the “feel-good chemical,” the “motivation molecule,” and even the “currency of pleasure.” While catchy, these nicknames oversimplify a very complex molecule. Dopamine is not just about feeling good — it’s about wanting, seeking, and acting. It’s the fuel behind your desire to get out of bed, chase your dreams, and savor life’s rewards.
Without dopamine, everyday life would lose its spark. Food would taste bland, your favorite hobbies would feel dull, and even getting through daily tasks would seem pointless. Too much dopamine, however, can cause impulsivity, risk-taking, or even severe mental health issues. In this guide, we’ll explore what dopamine really is, how it works, what happens when it’s out of balance, and how you can support healthy dopamine function for a motivated, balanced, and fulfilling life.
What is Dopamine?
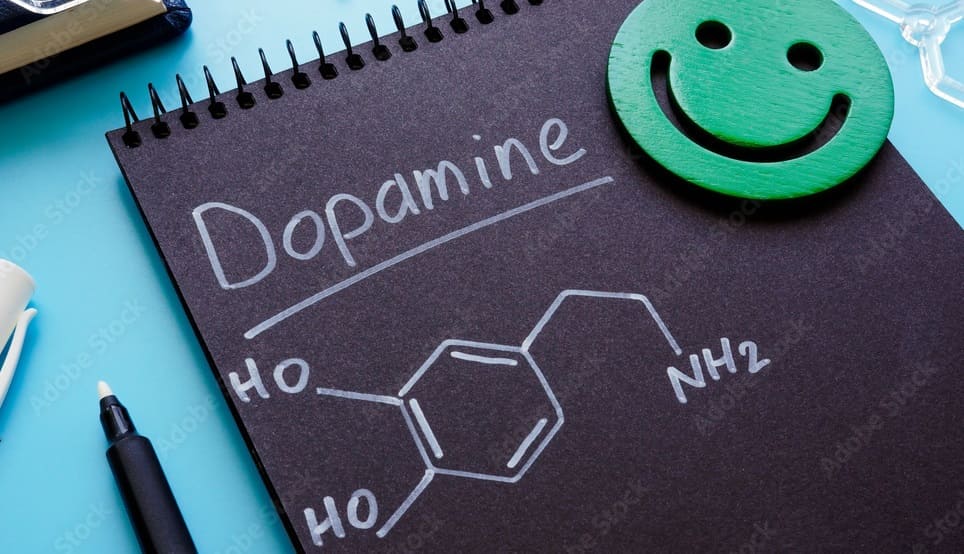
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter — a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain and the body. It belongs to the catecholamine family, alongside norepinephrine and epinephrine (adrenaline).
It is primarily produced in two brain regions:
- Substantia nigra (plays a key role in movement)
- Ventral tegmental area (VTA) (involved in reward and motivation)
Unlike serotonin, which makes you feel content, dopamine drives you toward a goal. It pushes you to take action, to get the reward — whether that’s finishing a project, eating a favorite meal, or winning a competition.
The Science of Dopamine: How It Works
Dopamine is central to the brain’s reward system. Imagine your brain as a motivational coach. When you do something enjoyable or beneficial — like exercising, eating, or socializing — dopamine is released. This release tells you, “That was good. Let’s do it again.”
But here’s the twist: dopamine spikes before you actually get the reward. This is called the anticipatory phase. For example:
- You see your favorite dessert → dopamine rises.
- You smell fresh coffee in the morning → dopamine rises.
- You hear the opening notes of your favorite song → dopamine rises.
This anticipatory nature makes dopamine a key driver of motivation and habit formation.
Four Dopamine Pathways in the Brain
Dopamine travels along four main pathways in the brain. Each pathway serves a unique function:
- Mesolimbic Pathway – Often called the “reward pathway.” It links the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens and is responsible for pleasure, reward learning, and motivation.
- Mesocortical Pathway – Connects the VTA to the prefrontal cortex. This pathway helps with decision-making, working memory, and planning.
- Nigrostriatal Pathway – Connects the substantia nigra to the striatum. It is critical for voluntary movement. Damage here is linked to Parkinson’s disease.
- Tuberoinfundibular Pathway – Runs from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland, regulating the release of the hormone prolactin.
Functions of Dopamine in the Body
While dopamine is often discussed in the context of mood and motivation, it has many other essential functions, both in the brain and throughout the body.
1. Motivation and Reward
Dopamine is central to the mesolimbic pathway, often called the brain’s “reward pathway.” This system reinforces behaviors that are beneficial for survival — such as eating, social bonding, and reproduction.
2. Motor Control
In the nigrostriatal pathway, dopamine plays a critical role in controlling movement. When dopamine-producing neurons in this pathway die off, it can lead to movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
3. Regulation of Prolactin
In the hypothalamus, dopamine inhibits the release of prolactin, a hormone involved in lactation and reproductive functions.
4. Cognition and Learning
Dopamine helps regulate attention, working memory, and decision-making. It’s crucial for reinforcement learning, where the brain learns from feedback.
5. Mood Regulation
Although not the only player, dopamine influences mood. Low dopamine activity can be linked to feelings of apathy, sadness, or lack of enthusiasm.
Causes of Dopamine Imbalance
Dopamine imbalance can be caused by:
1. Poor Diet and Nutrient Deficiency:
- Lack of protein-rich foods (which provide amino acids like tyrosine) can reduce dopamine production.
- Low intake of vitamins and minerals such as iron, magnesium, and vitamin B6 affects neurotransmitter synthesis.
2. Chronic Stress:
- Prolonged stress elevates cortisol, which can deplete dopamine levels over time.
- Stress also reduces the brain’s ability to produce and release dopamine efficiently.
3. Sleep Deprivation:
- Poor sleep quality or insufficient rest disrupts the brain’s natural dopamine cycles.
- Lack of REM sleep can lower dopamine receptor sensitivity.
4. Substance Abuse:
- Drugs like cocaine, methamphetamine, and even excessive alcohol initially spike dopamine but cause long-term depletion.
- Nicotine can also overstimulate dopamine receptors, leading to desensitization.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle:
- Physical inactivity reduces blood flow and neurochemical balance, affecting dopamine production.
6. Mental Health Disorders:
- Depression, ADHD, schizophrenia, and Parkinson’s disease are linked to abnormal dopamine activity.
- In some cases, the imbalance is a symptom, while in others it may be a contributing cause.
7. Hormonal Changes:
- Thyroid disorders, menopause, and low testosterone or estrogen can influence dopamine production and receptor activity.
8. Excessive Screen Time and Overstimulation:
- Overexposure to quick dopamine “hits” from social media, gaming, or gambling can lead to dopamine desensitization.
9. Chronic Inflammation:
- Inflammatory conditions and autoimmune disorders can damage brain cells and disrupt neurotransmitter balance.
10. Genetic Factors:
- Some people naturally produce more or less dopamine due to genetic variations in dopamine receptor genes.
Symptoms of Dopamine Imbalance
Here’s a symptoms of dopamine imbalance:
Low Dopamine Symptoms:
Low dopamine levels can make life feel dull, unmotivated, and draining.
Mental & Emotional Symptoms:
- Lack of motivation or drive
- Difficulty feeling pleasure (anhedonia)
- Low mood or mild depression
- Brain fog and poor concentration
- Reduced interest in hobbies or relationships
- Low self-confidence
Physical Symptoms:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Slow movements or stiffness
- Trouble initiating tasks
- Poor coordination
- Sleep problems (especially excessive sleepiness)
High Dopamine Symptoms:
Excess dopamine can overstimulate the brain, leading to impulsive or erratic behavior.
Mental & Emotional Symptoms:
- Restlessness and hyperactivity
- Impulsivity and risk-taking behavior
- Racing thoughts
- Increased aggression or irritability
- Heightened paranoia or suspiciousness
- In severe cases: hallucinations or delusions (linked to conditions like schizophrenia)
Physical Symptoms:
- Insomnia
- Increased heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Sweating or excessive alertness
Why Balance Matters?
Both low and high dopamine can negatively impact mental health, productivity, and relationships.
- Low dopamine often feels like “nothing matters.”
- High dopamine can feel like “everything is too much.”
Maintaining dopamine balance is key for stable mood, motivation, and cognitive function.
Dopamine-Related Disorders
1. Parkinson’s Disease
Characterized by the death of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to tremors, stiffness, and slow movement.
2. Schizophrenia
Often linked to excessive dopamine activity in some brain regions, causing hallucinations and delusions.
3. ADHD
May involve reduced dopamine signaling in the prefrontal cortex, leading to attention deficits.
4. Depression
Some forms involve low dopamine, especially those with apathy and low motivation.
5. Addiction
Drugs like cocaine and methamphetamine flood the brain with dopamine, rewiring reward pathways and creating dependency.
How Lifestyle Affects Dopamine?
The modern lifestyle — full of instant gratification through social media, processed foods, and quick entertainment — can overstimulate dopamine pathways. This can lead to dopamine tolerance, where your brain requires more stimulation to feel the same reward.
On the other hand, healthy habits like exercise, meaningful relationships, and balanced nutrition can support optimal dopamine levels.
Case Study: Dopamine and Motivation
Consider two employees:
- Alex: Sleeps well, exercises regularly, eats protein-rich meals, and sets small achievable goals. His dopamine system works in balance — he feels motivated, focused, and satisfied.
- Jordan: Stays up late, consumes lots of sugar, relies on energy drinks, and spends hours on social media. His dopamine system is overstimulated, making everyday tasks feel dull and unrewarding.
This contrast shows how lifestyle directly affects dopamine balance and motivation.
How to Increase Dopamine Levels Naturally?
Dopamine plays a major role in motivation, focus, mood, and pleasure. If you’ve been feeling unmotivated, unfocused, or generally “flat,” you might be experiencing low dopamine activity. The good news is — there are many ways to naturally boost dopamine without relying on quick fixes or unhealthy habits. Here’s a complete guide.
1. Eat Dopamine-Boosting Foods
Dopamine is made from the amino acid tyrosine, found in protein-rich foods.
Best Sources of Tyrosine:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef)
- Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Eggs
- Dairy products (cheese, milk, yogurt)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, soybeans)
Other Nutrients That Help:
- Vitamin B6, B9, B12 – Help convert tyrosine to dopamine
- Magnesium – Regulates neurotransmitter activity
- Omega-3 fatty acids – Improve dopamine receptor sensitivity
- Vitamin D – Supports dopamine production and receptor health
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercise increases dopamine release and receptor sensitivity, making your brain more responsive to dopamine.
Best Types of Exercise for Dopamine:
- Aerobic activities (running, cycling, swimming)
- Strength training
- Dancing
- Team sports
- Even a brisk 20-minute walk can help
Tip: Exercise outdoors for an extra boost from sunlight.
3. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep lowers dopamine receptor sensitivity. Aim for 7–9 hours of restful sleep.
Sleep Tips for Dopamine Health:
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
- Avoid heavy screen time before bed.
- Keep your room dark, quiet, and cool.
4. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Meditation helps regulate dopamine release and reduces stress, which can otherwise deplete dopamine levels.
Simple Practice:
- Sit comfortably.
- Focus on your breath for 5–10 minutes.
- Gently return your attention when your mind wanders.
5. Engage in Creative Activities
Creativity triggers dopamine release because it involves challenge, novelty, and reward.
Ideas:
- Painting, drawing, writing
- Playing an instrument
- Cooking a new recipe
- Building or crafting something
6. Listen to Music You Love
Music you enjoy — especially songs that give you chills — can trigger dopamine release in the brain’s reward centers.
Tip: Curate a playlist of songs that make you feel energized and inspired.
7. Get Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight boosts dopamine and also helps your body produce vitamin D, which is essential for dopamine receptor function.
- Aim for 15–30 minutes of sun exposure in the morning.
- On cloudy days, consider a vitamin D supplement (check with your doctor).
8. Limit Overstimulation
Constant dopamine spikes from social media, junk food, and video games can desensitize your brain’s dopamine receptors.
How to Reduce Overstimulation:
- Set screen time limits.
- Replace high-dopamine junk food with healthy snacks.
- Take regular breaks from technology.
9. Try Cold Exposure
Cold showers or ice baths can increase dopamine levels significantly and keep them elevated for hours.
Beginner’s Tip:
- Start with 30 seconds of cold water at the end of your shower.
- Gradually increase to 2–3 minutes.
10. Break Goals Into Small Wins
Dopamine spikes when you achieve a goal — even a small one.
Strategy:
- Set small, achievable goals.
- Celebrate progress, no matter how minor.
- Use a checklist to track completed tasks.
11. Connect Socially
Positive social interaction releases dopamine and other feel-good neurotransmitters like oxytocin.
Ideas:
- Spend time with friends or family.
- Join a group or club.
- Volunteer for a cause you care about.
12. Consider Natural Supplements
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, certain supplements may help — but consult your doctor first.
Common Options:
- L-Tyrosine – Direct dopamine precursor
- Mucuna pruriens – Natural source of L-DOPA
- Omega-3s – Improve receptor sensitivity
- B-vitamins – Aid dopamine synthesis
7-Day Dopamine-Friendly Lifestyle Plan
Here’s a 7-day dopamine-friendly lifestyle plan designed to naturally balance and boost your dopamine levels without causing overstimulation. It focuses on nutrition, exercise, creativity, social connection, and rest — the pillars of healthy dopamine function.
Day 1 – Kickstart Motivation
Morning:
- 15 min sunlight exposure
- Protein-rich breakfast (eggs, spinach, whole grain toast)
- 20-min brisk walk
Afternoon:
- Work in 50-min focused blocks with 10-min breaks
- Lunch: grilled chicken, quinoa, and roasted vegetables
- Short creative activity (sketch, write, or plan something)
Evening:
- Social call with a friend
- Dinner: salmon, sweet potato, and green beans
- 5-min gratitude journaling before bed
Day 2 – Movement & Mood
Morning:
- Stretch for 10 min
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with nuts and berries
- 15-min meditation session
Afternoon:
- Lunch: turkey and avocado wrap
- Listen to upbeat music while working
- Take a 15-min walk outside
Evening:
- Strength training or home workout (30 min)
- Dinner: grilled tofu, brown rice, and steamed broccoli
- Read a chapter from a non-work-related book before bed
Day 3 – Creativity Boost
Morning:
- Morning sunlight
- Breakfast: oatmeal with banana and chia seeds
- 10-min breathing exercises
Afternoon:
- Lunch: lentil soup with whole grain bread
- Engage in a hobby (painting, writing, or photography)
- Short break to watch something inspiring (TED talk, documentary)
Evening:
- Meet a friend in person or join a group activity
- Dinner: baked fish, quinoa, and roasted carrots
- Write 3 small wins of the day before sleep
Day 4 – Social & Sensory Balance
Morning:
- Cold shower (30–60 seconds)
- Breakfast: scrambled eggs, avocado, and tomato
- 10-min gratitude journaling
Afternoon:
- Lunch: chickpea salad with olive oil dressing
- Listen to music while doing focused work
- Step outside for fresh air and light walking
Evening:
- Volunteer or do a kind act for someone
- Dinner: chicken stir-fry with vegetables
- Wind down with gentle stretching or yoga
Day 5 – Nature Connection
Morning:
- Walk in a park or natural area
- Breakfast: cottage cheese with pineapple and walnuts
- Light bodyweight workout (15–20 min)
Afternoon:
- Lunch: tuna salad with whole wheat crackers
- Spend 15 min learning something new
- Keep hydrated — at least 2 liters of water today
Evening:
- Dinner: grilled vegetables with lean protein of choice
- No screens 1 hour before bed — replace with reading
- Deep breathing for 5 min before sleeping
Day 6 – Rest & Reset
Morning:
- Slow wake-up with stretching
- Breakfast: smoothie (spinach, banana, protein powder, almond milk)
- 10-min mindful breathing session
Afternoon:
- Lunch: baked salmon with couscous and spinach
- Watch a comedy or uplifting film (laughter boosts dopamine)
- Short walk in sunlight
Evening:
- Dinner: vegetable curry with brown rice
- Reflect on the week and plan small goals for next week
- Go to bed early for full rest
Day 7 – Achievement Day
Morning:
- Cold exposure (shower or splash)
- Breakfast: omelet with mushrooms and onions
- Write down top 3 goals for the day
Afternoon:
- Lunch: turkey burger with salad
- Complete a challenging but rewarding task
- Celebrate with a non-food reward (new book, flowers, etc.)
Evening:
- Dinner: baked chicken with roasted Brussels sprouts
- Spend time with loved ones
- End the night with meditation and gratitude journaling
Key Rules Throughout the Week
- Protein in every meal – supports dopamine production
- Daily movement – at least 20 min
- Sunlight exposure – for vitamin D and mood
- Mindfulness practice – 5–10 min daily
- Limited screen use – avoid constant dopamine spikes
- Small goals – for steady motivation rewards
7-Day Dopamine-Friendly Meal Plan
Here’s a 7-Day Dopamine-Friendly Meal Plan designed to naturally support dopamine production by including foods rich in tyrosine (dopamine’s building block), antioxidants, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
This plan avoids excess sugar and processed foods that can cause dopamine spikes followed by crashes.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Snack | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spinach & mushroom omelet + whole-grain toast + green tea | Grilled salmon with quinoa, steamed broccoli & carrots, side salad | Walnuts + blueberries | Chicken breast stir-fry with bell peppers & zucchini + brown rice |
| 2 | Greek yogurt with chia seeds, banana, honey + herbal tea | Turkey & avocado lettuce wraps + mixed greens salad | Cottage cheese + pineapple chunks | Lentil soup + roasted sweet potatoes + steamed asparagus |
| 3 | Oatmeal with almonds, pumpkin seeds, strawberries + optional black coffee | Baked mackerel with wild rice + roasted Brussels sprouts | Apple slices + peanut butter | Grass-fed beef stir-fry with bok choy & bell peppers + cauliflower rice |
| 4 | Scrambled eggs with smoked salmon & spinach + whole-grain toast + green tea | Chickpea salad with olive oil, parsley, cherry tomatoes, lemon | Almonds + dark chocolate (70%+) | Grilled chicken + mashed sweet potatoes + steamed broccoli |
| 5 | Smoothie: spinach, banana, almond butter, flaxseeds, almond milk | Quinoa & black bean bowl + avocado + lime dressing | Boiled egg + cucumber slices | Baked trout + roasted root vegetables (carrots, beets, parsnips) |
| 6 | Greek yogurt with walnuts, blueberries, cinnamon | Turkey chili with kidney beans & bell peppers | Celery sticks + hummus | Grilled lamb chops + garlic sautéed spinach + couscous |
| 7 | Mushroom & spinach frittata + avocado slices + herbal tea | Grilled chicken Caesar salad (yogurt-based dressing) | Pumpkin seeds + orange slices | Baked salmon + quinoa + steamed green beans |
Tips for Dopamine-Friendly Eating
- Include protein-rich foods at each meal to provide tyrosine for dopamine production.
- Add colorful fruits and vegetables for antioxidants that protect dopamine-producing neurons.
- Use healthy fats (olive oil, avocado, nuts) for brain health.
- Limit processed sugar and refined carbs to avoid dopamine crashes.
Supplements That May Support Dopamine
Before taking any supplement, consult a healthcare professional. Options include:
- L-Tyrosine – Direct precursor to dopamine
- Mucuna pruriens – Contains natural L-DOPA
- Omega-3 fatty acids – Support brain health
- Vitamin D, B6, B12 – Cofactors in dopamine production
- Magnesium – Helps regulate neurotransmitter activity
Dopamine and Habits
Dopamine is deeply tied to habit formation. The cue-routine-reward cycle works because dopamine reinforces the reward, making you repeat the behavior.
Example:
- Cue: Seeing running shoes by the door
- Routine: Going for a jog
- Reward: Dopamine release from exercise
Over time, the cue itself triggers dopamine in anticipation of the reward, making the habit automatic.
Dopamine Fasting: Does It Work?
The concept of “dopamine fasting” has gained popularity, especially in tech circles. The idea is to reduce overstimulation by avoiding activities that trigger dopamine spikes — like social media, junk food, and video games — for a set period.
While you can’t literally “fast” from dopamine (your brain produces it constantly), reducing overstimulation can help reset reward pathways, making everyday activities feel more satisfying.
Dopamine and Mental Health
Balanced dopamine function supports:
- Stable mood
- Motivation
- Resilience to stress
- Healthy reward processing
On the other hand, chronic dopamine imbalance may contribute to depression, anxiety, and mood instability.
Myths About Dopamine
Myth 1: Dopamine is just about pleasure.
Truth: It’s more about motivation and anticipation than the pleasure itself.
Myth 2: More dopamine is always better.
Truth: Both excess and deficiency can cause problems.
Myth 3: You can completely “reset” your dopamine in a few days.
Truth: Dopamine regulation is ongoing and influenced by long-term habits.
Long-Term Dopamine Health Plan
Morning Routine
- Wake up with sunlight exposure.
- Eat a protein-rich breakfast.
- Engage in light exercise.
Daytime
- Break work into achievable goals.
- Take short active breaks.
- Stay hydrated and eat balanced meals.
Evening
- Avoid heavy screen use 1 hour before bed.
- Practice relaxation techniques.
- Sleep at a consistent time.
Dopamine vs. Serotonin: Not the Same Thing
Many people confuse dopamine with serotonin because both are linked to mood. But their functions differ:
| Feature | Dopamine | Serotonin |
|---|---|---|
| Main Role | Motivation, reward, drive | Mood stability, well-being |
| Effect | Encourages action | Encourages contentment |
| Production Sites | Substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area | Raphe nuclei |
| Imbalance Effects | Low drive, Parkinson’s, ADHD | Depression, anxiety, insomnia |
In short, dopamine drives you to want things, while serotonin helps you enjoy them once you have them.
Conclusion
Dopamine is much more than a “feel-good” chemical. It’s a powerful motivator, a teacher, and a guide that shapes our actions, habits, and even our survival. Keeping it balanced is key to living a productive, joyful, and healthy life. By understanding dopamine’s role and nurturing it through diet, lifestyle, and mindful habits, you can harness its full potential without falling into the trap of overstimulation or burnout.
FAQ’s
When is dopamine released?
Dopamine is released when the brain anticipates or experiences something rewarding, such as achieving a goal, eating enjoyable food, or engaging in pleasurable activities. It’s also triggered by novelty, learning, and certain social interactions that the brain perceives as positive or motivating.
Does sugar affect dopamine?
Yes, Sugar causes dopamine spikes, which can lead to cravings and dependency.
Is low dopamine permanent?
Not necessarily, Lifestyle changes can often restore balance unless caused by a neurological disease.
How quickly can you improve dopamine health?
You may notice changes within weeks, but long-term balance requires consistent habits.
Does music affect dopamine?
Yes, Listening to music you enjoy can increase dopamine release and boost mood.
What happens when dopamine levels are too low?
Low dopamine can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, lack of motivation, depression, difficulty concentrating, and, in severe cases, conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
What happens when dopamine levels are too high?
Excess dopamine can cause restlessness, impulsive behavior, hyperactivity, and, in extreme cases, contribute to psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia or mania.
What foods help boost dopamine naturally?
Foods rich in tyrosine (an amino acid) help increase dopamine production. These include eggs, lean meats, fish, dairy products, bananas, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
Can exercise improve dopamine levels?
Yes, Regular physical activity, especially aerobic exercises like jogging, swimming, and cycling, can increase dopamine production and receptor sensitivity.
Is dopamine the same as serotonin?
No, While both are neurotransmitters, dopamine is primarily linked to motivation and reward, whereas serotonin is more associated with mood stability and overall well-being.
Does drinking coffee increase dopamine?
Yes, caffeine temporarily increases dopamine signaling, which can enhance alertness and mood. However, excessive consumption may lead to dependency and reduced sensitivity over time.
Can you test your dopamine levels?
Direct testing in the brain is not practical for routine use, but doctors may assess dopamine-related function through symptom evaluation, imaging scans, or by testing related hormones and neurotransmitters.
Does sleep affect dopamine?
Absolutely, Quality sleep helps regulate dopamine production and receptor activity. Poor sleep can significantly lower dopamine levels.
How long does it take to restore healthy dopamine levels?
It depends on the cause of the imbalance. For mild deficiencies caused by lifestyle factors, noticeable improvement can occur within weeks of healthy changes. For medical conditions, treatment may take months and require professional supervision.
What does dopamine do for you?
Dopamine helps regulate mood, motivation, focus, learning, movement, and the brain’s reward system. It makes you feel driven to achieve goals and experience pleasure from rewarding activities.
How to tell if dopamine is low?
Common signs of low dopamine include fatigue, low motivation, sadness, difficulty focusing, loss of interest in activities, sugar cravings, and, in severe cases, movement difficulties.
Is dopamine a happy hormone?
Yes, dopamine is often called a “happy hormone” because it plays a key role in feelings of pleasure and reward. However, it’s more about motivation and drive than long-term happiness, which is more influenced by serotonin.
Which vitamin boosts dopamine?
Vitamin B6, B12, and folate help in dopamine production. Vitamin D also supports healthy dopamine levels by influencing brain function.
How to check dopamine levels at home?
There is no accurate at-home test for dopamine levels. The best way is to monitor symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation through clinical assessment or specialized lab tests.
Also Read: