What is Arthritis ?
Arthritis is a broad term used to describe a group of disorders characterized by inflammation of the joints. This condition can affect people of all ages, from children to the elderly, and it encompasses more than a hundred different types. The most prevalent forms of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis, is the most common type. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. This leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joints. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine. It is often associated with aging, joint overuse, or joint injuries.
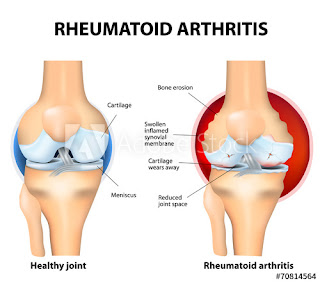
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. This leads to chronic inflammation, pain, and sometimes deformity. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis can affect multiple joints simultaneously and can also involve other body systems. It is a systemic condition that can lead to fatigue, fever, and overall malaise.
In addition to osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, there are various other forms of arthritis, such as psoriatic arthritis, gout, and lupus-related arthritis. These conditions have different underlying causes and unique patterns of joint involvement. While some forms of arthritis have a known genetic predisposition, others may be triggered by infections or environmental factors.
The impact of arthritis on an individual’s daily life can be significant. Chronic pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility can limit one’s ability to perform routine tasks, engage in physical activities, and even lead to a decreased quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in minimizing the progression of arthritis and improving the overall well-being of affected individuals. Treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, surgery. With proper care and support, many individuals with arthritis can lead active and fulfilling lives.
Types of Arthritis
There are over a hundred different types of arthritis, each with its own distinct characteristics, causes, and treatment approaches. Here are some of the most common types of arthritis:
1) Osteoarthritis (OA):
Also known as “wear and tear” arthritis, OA is the most prevalent form. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joints. Commonly Affected Joints: Hands, knees, hips, and spine.
2) Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
RA is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation, pain, and sometimes deformity. It can also affect other body systems. Commonly Affected Joints: Multiple joints, often symmetrical.
3) Psoriatic Arthritis:
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of arthritis that can develop in individuals with psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. It affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling, and may also involve the nails and other tissues. Commonly Affected Joints: Any joint, including fingers and toes.
4) Gout:
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. This leads to sudden and severe pain, often in the big toe, along with swelling and redness. Commonly Affected Joints: Often the big toe, but can affect any joint.
5) Lupus-Related Arthritis (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – SLE):
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation in various parts of the body, including the joints. Joint pain and stiffness are common symptoms in individuals with lupus. Commonly Affected Joints: Multiple joints, often associated with other systemic symptoms.
6) Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation and pain in the vertebrae. It can also lead to the fusion of spinal joints, resulting in a stooped posture. Commonly Affected Joints: Spine, sacroiliac joints (where the spine meets the pelvis).
7) Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA):
JIA refers to several types of arthritis that develop in children under the age of 16. It is an autoimmune condition that causes joint inflammation, often leading to joint damage and disability if not managed properly. Commonly Affected Joints: Variable, but knees and wrists are often involved.
8) Infectious Arthritis:
This type of arthritis is caused by an infection in the joint. It can occur due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi entering the joint space, leading to inflammation and pain. Commonly Affected Joints: Variable, depending on the specific infectious agent.
Causes of Arthritis
Here are the common causes of arthritis:
1) Osteoarthritis (OA):
Results from the gradual wear and tear of joint cartilage over time, often due to aging or repetitive joint use.
2) Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
Arises from an autoimmune response where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own joints, leading to inflammation and damage.
3) Psoriatic Arthritis:
Develops in individuals with psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition, due to an abnormal immune response affecting joints and tissues.
4) Gout:
Occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the body, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints, causing inflammation.
5) Lupus-Related Arthritis (SLE):
Part of the systemic autoimmune disease lupus, where the immune system attacks various tissues including joints, resulting in inflammation.
6) Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Stemming from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, it primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints.
7) Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA):
An autoimmune condition affecting children, the exact cause is unknown, but it likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
8) Infectious Arthritis:
Arises from an infection within a joint, often due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi entering the joint space, causing inflammation.
9) Metabolic Arthritis (e.g., Pseudogout):
Results from the buildup of calcium crystals in the joints, leading to sudden pain and inflammation.
10) Traumatic Injury:
Joint injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can lead to post-traumatic arthritis, where damage to the joint surface accelerates the development of arthritis.
11) Hormonal Factors (e.g., Hormonal Arthritis during Menopause):
Changes in hormonal levels, particularly during menopause, can contribute to joint pain and inflammation.
12) Genetic Predisposition:
Some forms of arthritis, like ankylosing spondylitis, have a genetic component, making individuals more susceptible to developing the condition.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Here are the common symptoms of arthritis:
- Joint Pain: Persistent discomfort or aching in one or more joints.
- Swelling: Visible or palpable swelling around affected joints.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Redness and Warmth: Inflamed joints may appear reddened and feel warm to the touch.
- Tenderness: Sensitivity or pain when pressure is applied to the joint.
- Fatigue: Often accompanies inflammatory types of arthritis, leading to overall tiredness.
- Morning Stiffness: Joints may be particularly stiff upon waking and improve with movement.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty performing daily activities due to joint pain and stiffness.
- Deformities: In advanced cases, joints may become misshapen or appear swollen.
- Fever and Malaise: Systemic symptoms can occur with certain types of inflammatory arthritis.
- Skin Changes (in Psoriatic Arthritis): Scaly, red patches of skin may accompany joint symptoms.
- Nail Changes (in Psoriatic Arthritis): Pitting, discoloration, or separation of the nail from the nail bed.
- Eye Problems (in some forms of Arthritis): Such as uveitis or redness and pain in the eyes.
Prevention Tips for Arthritis
- Excess weight puts strain on joints, so aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Engage in regular, low-impact exercises to strengthen muscles and support joint health.
- Use proper techniques and equipment when engaging in physical activities to prevent injuries.
- Take breaks and practice ergonomics to reduce strain on joints during repetitive tasks.
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 rich fish in your diet.
- Proper hydration supports joint lubrication and overall bodily function.
- Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to the development of certain types of arthritis.
- Chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms, so practice stress-reducing techniques.
- Use supportive footwear and consider joint-friendly tools or aids for daily tasks.
- Early detection and treatment of arthritis can help prevent its progression.
- Seek professional advice for personalized prevention strategies based on your health profile.
Ayurvedic Treatment and Medicine for Arthritis
Following ayurvedic remedies may recommend for people with Arthritis :
- In the morning, boil one putty garlic in half a kilo of milk. When half a loaf of milk remains, filter it and drink it. On the second day two garlic cloves, on the third day three garlic cloves, in the same way, on the eleventh day, on the eleventh day, boil eleven one putty garlic in milk and filter it and drink the milk. From the twelfth day onwards reduce the number of garlic one by one.
- Boil 10 grams of Punarnavaki root in 100 grams of water and drink it after filtering 25 grams remaining.
- Take two tablets of Yograj Guggul with hot water in the morning and evening.
- Ashwagandha, Chopchini, Peepalmool, Dry ginger- Drink equal quantity of its powder with milk in the morning and evening.
- After baking at the joints, apply ghee on the ready leaves and tie them.
- Swallow 10 grams fenugreek seeds at bedtime and drink water.
- Massage Narayan oil on the place of pain.
Home Remedies for Arthritis
Here are some natural remedies for arthritis:
1) Turmeric and Curcumin:
Turmeric, a spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, contains a compound called curcumin known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with. It can be added to food or taken as a supplement.
2) Ginger:
Ginger is another spice with natural anti-inflammatory properties. It contains compounds like gingerol that can help reduce pain and swelling in arthritic joints. Ginger can be added to meals, brewed as a tea, or taken in supplement form.
3) Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects. Consuming these foods or taking fish oil supplements can help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
4) Glucosamine and Chondroitin:
These natural compounds are found in the cartilage of animals. They are commonly taken in supplement form to support joint health and may help alleviate symptoms, although results vary among individuals.
5) Boswellia:
Also known as Indian frankincense, Boswellia is an herbal extract that may have anti-inflammatory effects. It can be taken in supplement form and has shown promise in reducing pain and improving joint function in some studies.
6) Vitamin D:
Adequate vitamin D levels are essential for maintaining healthy bones and joints. Spending time in sunlight, consuming vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, or taking supplements can help support joint health.
7) Capsaicin Cream:
Capsaicin is a compound found in chili peppers known for its pain-relieving properties. Applying capsaicin cream topically can provide temporary relief from joint pain by inhibiting pain signals.
8) Massage and Physical Therapy:
Gentle massage and targeted physical therapy exercises can help improve joint mobility, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain associated with arthritis.
9) Epsom Salt Baths:
Soaking in a warm bath with Epsom salts can help relax muscles and reduce joint stiffness. The magnesium in Epsom salts may also have anti-inflammatory effects.
10) Heat and Cold Therapy:
Applying warm compresses or using heating pads can help relax muscles and ease joint stiffness. Cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing pain relief.
It’s important to note that while natural remedies can be beneficial for some individuals, they may not work for everyone, and their effectiveness can vary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or herbal remedies, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking medications. Additionally, if symptoms persist or worsen, seeking professional help is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diet for Arthritis
Consumption of items like wheat, millet, roti, fenugreek, amaranth, bitter gourd, tinda, apple, papaya, grapes, dates, garlic etc. is beneficial.
Foods to Avoid
Rice, potato, cabbage, radish, beans, gram, urad dal, banana, orange, lemon, guava, tomato, curd and all air-borne substances, diabetic, over-exertion, etc. increase the disease.
