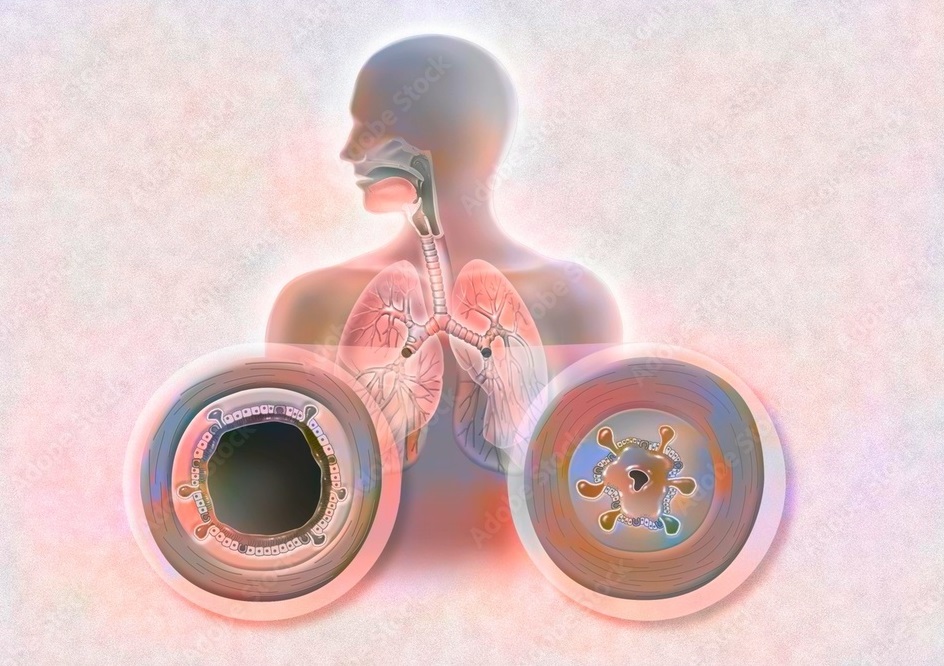
What is Bronchitis ?
Bronchitis is an inflammatory disease of the trachea. Bronchitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the bronchial tubes, causing them to become swollen and produce excess mucus. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting). The tubes that carry air from the trachea to the lungs are called bronchi. In this, the walls of the bronchi become unnecessarily weak due to infection and inflammation, due to which their shape becomes like a balloon. Due to this swelling, more mucus is produced than normal, as well as these walls are unable to push out the accumulated mucus. As a result of this, there is a severe accumulation of thick mucus in the airways, which creates blockage in the tubes. The lungs and breathing tubes located in the damaged part are not able to do their work smoothly and various complications arise in the patient’s body.
Exposure to infection due to improper diet, lifestyle or weak immunity leads to problems like bronchitis. It is an inflammatory disease occurring in the airways, in which all the three doshas become deformed and cause the disease. Bronchitis is called Bronchitis in Ayurveda, mainly due to aggravation of Pitta dosha and Vata and Kapha dosha are also imbalanced.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis
The passage through which the breath enters and leaves your lungs is called the trachea. If your trachea becomes irritated and inflamed, you may have bronchitis. This is a kind of stimulation due to which the trachea makes more mucus.
Sometimes, you may also need to have a chest X-ray, sputum or lung tests to rule out bronchitis.

Symptoms of Bronchitis
Apart from cough, there are other symptoms of bronchitis, but its symptoms also vary according to the type :
- Cough
- Lack of energy
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Slight fever and chills
- Chest discomfort
- Wheezing sound when breathing
- Blocked nose and sinuses
- Production of mucus (sputum)
- Sore throat.
- Tiredness
- Vomiting
Types of Bronchitis
There are generally two types of bronchitis :
1) Acute Bronchitis :
Acute Bronchitis is short-lived that develops after a viral disease such as the flu or a cold. Symptoms include chest discomfort or pain with mucus, fever, and sometimes shortness of breath.
Acute bronchitis is a short-term illness caused by an infection or a cold. Whereas, chronic bronchitis is of longer duration and may result in progression of the disease.
Although acute bronchitis can occur in a person of any age, it is more common in young children. Children are more susceptible to infection, so they are also more likely to develop acute bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis can affect men and women of any age, but it is most common in middle-aged men.
2) Chronic Bronchitis :
It continues for a few weeks to months. This is due to excessive smoking. Chronic bronchitis becomes a problem even after repeated occurrences of acute bronchitis.
This is the most common condition that develops in COPD if left untreated in chronic. Due to this the damage done to the lungs cannot be repaired again. In chronic, the bronchial tubes become inflamed and constrict. This causes more mucus to build up in the lungs which can further block the narrowed tubes.
Causes of Bronchitis
It can be caused by various factors, including:
1) Viral Infections: The most common cause of acute bronchitis is viral infections, particularly the influenza virus (flu) and rhinoviruses (common cold).
2) Bacterial Infections: While less common, bacterial infections, such as those caused by bacteria like Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Bordetella pertussis (whooping cough), can lead to it.
3) Environmental Irritants: Prolonged exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke, air pollution, dust, fumes, or chemical vapors can irritate the bronchial tubes, leading to chronic bronchitis.
4) Allergies: Allergens like pollen, mold, pet dander, or certain chemicals can trigger allergic reactions that contribute to bronchitis in susceptible individuals.
5) Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): In some cases, stomach acid backing up into the esophagus can enter the airways, causing irritation and leading to bronchitis symptoms.
6) Respiratory Conditions: Pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase the risk of developing it.
7) Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, or organ transplant recipients may be more susceptible to bronchitis.
8) Inhalation of Harmful Substances: Exposure to toxic substances like asbestos, chemical solvents, or industrial pollutants can lead to bronchitis.
9) Fungal Infections: While rare, certain types of fungi, such as Aspergillus, can cause fungal bronchitis in individuals with weakened immune systems.
10) Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to bronchitis, especially if it runs in their family.
Prevention Tips for Bronchitis
- Use polyunsaturated fats and soap grains in food.
- Consume almonds and walnuts in nuts.
- Drink plenty of fluids, herbal teas and soups.
- Eat raw onion, it has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Eat all types of berries, spinach and carrots among fruits. It is rich in anti-oxidants.
- Garlic and ginger have the ability to strengthen the immune system, so consume them in proper quantity in the food.
- Smoking is the main reason for this, so give it up completely.
- Do not consume caffeinated beverages.
- Avoid irritants present in the air.
- Do not consume milk and dairy products.
- Don’t drink alcohol.
Effective Home Remedies for Bronchitis
Here are some home remedies that may help alleviate bronchitis symptoms:
1) Fresh basil leaves from 7 to 11 units or 1 gram (quarter teaspoon) powder of dry basil leaves, 2 grams of fresh ginger or half a gram powder of dry dry ginger, 7 pieces of black pepper crushed a little, 200 grams of these three things Put in boiling water and boil for 2 minutes. After that take it down and keep the lid for 2 minutes. After filtering after 2 minutes, add 100 grams of boiled milk and 1-2 teaspoons of sugar candy or sugar, drink it hot and cover it with a cloth and lie down for 5-10 minutes.
By this use, cold headache, cold in the nose, cold, sinus, inflammation and pain in the respiratory tract (bronchitis), common fever, malaria, indigestion etc. diseases are removed. Due to this, the accumulated phlegm of the chest becomes loose and comes out. Chest tightness and rib pain due to cold also goes away. Give the children half the amount in the tea. Take twice a day or as needed for 2-3 days.
2) Make a powder by grinding these three medicines separately, turmeric, dry ginger and black pepper and take 4-4 spoons of each powder and mix it in a single airtight (with cork or lid) and keep it safe by filling it in a clean vial. . Take half teaspoon (2 grams) of this medicine twice a day with the help of hot water. Apart from bronchitis, this use is also beneficial in cough, joint pain, backache, hip colic (pain of buttock or hip). Use as needed for 3 days to 7 days.
Note : If there is no full benefit then this experiment can be done for another 4-5 days.
3) Honey has natural antibacterial properties and is effective in soothing a sore throat. You can mix one to two teaspoons of honey with warm water or herbal tea. Note that honey should not be given to children under one year of age due to the risk of botulism.
4) Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. To make ginger tea, steep fresh ginger slices in hot water for about 10 minutes. You can add honey and lemon for added benefits.
5) Turmeric contains curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Incorporate turmeric into your cooking or mix it with warm milk for a soothing drink.
6) Using a humidifier or cool-mist vaporizer in your room adds moisture to the air, which can help ease congestion and reduce irritation in the throat and airways.
7) Gargling with warm saltwater can help soothe a sore throat, reduce inflammation, and clear mucus. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water, gargle for 15-30 seconds, and then spit it out.
8) Inhaling steam helps moisturize and soothe the airways. Boil a pot of water, remove it from the heat, and carefully inhale the steam while covering your head with a towel. You can also take a warm shower in a closed bathroom for similar effects.
9) Garlic is a natural antibiotic and immune booster. Adding garlic to your meals can help support your body’s defenses against infections.
10) Eucalyptus oil contains compounds that can help open up airways. Add a few drops of eucalyptus oil to a bowl of hot water, cover your head with a towel, and inhale the steam.
While home remedies can provide relief, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice and treatment. If you suspect you have bronchitis, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
When to See a Doctor ?
Acute bronchitis gets cured on its own with proper home treatment and diet, but if cough, fever, body ache, nasal congestion persist for more than two weeks, then a doctor should be consulted immediately. Apart from this, excessive mucus formation or bleeding while coughing, wheezing sound on breathing are the symptoms of chronic bronchitis. Even if you see any of these symptoms, you should immediately start treatment with a doctor. Otherwise, this condition can become serious and turn into chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
FAQ’s
Is Bronchitis contagious?
Acute bronchitis, which is often cause by viruses, can be contagious. It can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Chronic bronchitis, typically associated with smoking, is not contagious.
Can Bronchitis lead to more serious health issues?
In some cases, untreated or poorly managed bronchitis can lead to complications like pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly or those with weakened immune systems.
What is the treatment for Bronchitis?
Treatment for acute usually involves rest, staying hydrated, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. If bacterial infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribe. Chronic management focuses on lifestyle changes, like quitting smoking, and sometimes the use of bronchodilators or other medications.
How long does Bronchitis typically last?
Acute bronchitis symptoms can last for several weeks, but most cases improve within a few days to a week. Chronic is a long-term condition that persists for at least three months over two consecutive years.
Is Bronchitis more common in certain populations?
While anyone can develop bronchitis, those at higher risk include smokers, people with weakened immune systems, infants and young children, and the elderly.
Recommended Articles :